ARE YOU LOOKING FOR RELIABLE CIS 663 BIOMETRICS ASSIGNMENT HELP SERVICES? EXPERTSMINDS.COM IS RIGHT CHOICE AS YOUR STUDY PARTNER!
CIS 663 Biometrics - Syracuse University
Question 3. Perform a singularity detection in the following data. Use the definitions used in week 3 live session slides. Your answer should include all missing values in the table and the type of singularity detected.
|
k
|
θ
|
δ
|
Δ
|
|
0
|
80
|
|
|
|
1
|
90
|
|
|
|
2
|
260
|
|
|
|
3
|
50
|
|
|
|
4
|
110
|
|
|
|
5
|
270
|
|
|
|
6
|
130
|
|
|
|
7
|
180
|
|
|
Use the following two equations to fill in the column titled δ and the column titled Δ.
δ (k)= θ ((k +1)mod N )- θ (k)
δ (k) if |δ (k)|< Π/2
Δ(k) = δ (k)+Π if δ (k) ≤ -Π/2
δ (k)-Π if δ (k) ≥ Π/2
Once you have filled in the table give the type of singularity you believe is being represented based on:
360, then whorl
180, then loop
∑k∈(0...7} Δ(k) = - 180, then delta
0, then singularity
Answer:
|
k
|
θ
|
∂
|
Δ
|
|
0
|
80
|
560
|
0
|
|
1
|
90
|
1170
|
1170
|
|
2
|
260
|
4940
|
9880
|
|
3
|
50
|
1250
|
3750
|
|
4
|
110
|
3410
|
13640
|
|
5
|
270
|
9990
|
49950
|
|
6
|
130
|
5590
|
33540
|
|
7
|
180
|
8820
|
61740
|
At the point when the wavelet is the nth subordinate of a gaussian, the maxima bends are associated and experience the majority of the better scales. The rot rate of the maxima along the bends demonstrate the request of the separated singularities.
HIRE PROFESSIONAL WRITER FROM EXPERTSMINDS.COM AND GET BEST QUALITY CIS 663 BIOMETRICS ASSIGNMENT HELP AND HOMEWORK WRITING SERVICES!
Question 4. Determine the 3x3 binary pixel grid for:
a) A bifurcation point;
b) A non-minutiae point
(In live session we displayed and discussed the grid for the termination case).
For each specify:
- The values of b0 , ... , b7 for each case.
- What are their crossing numbers?
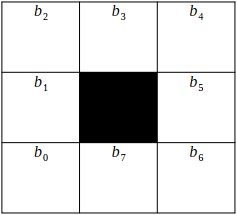
Crossing Number = ∑i∈(1...7)|bi - b(i+1)mod8|
Answer:
The most regularly utilized strategy for particulars extraction in this classification is the Crossing Number (CN) idea. An enormous number of methods for particulars extraction accessible in the writing have a place with this class. This strategy is supported over different techniques for its computational proficiency and natural straightforwardness. This technique includes the utilization of the skeleton picture where the edge stream example is eight-associated. The particulars are extricated by checking the nearby neighbouhood of each edge pixel in the picture utilizing a 3X3 window.
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
|
B1
|
B
|
B5
|
|
B0
|
B7
|
B6
|
WE HELP STUDENTS TO IMPROVE THEIR GRADES! AVAIL TOP QUALITY CIS 663 BIOMETRICS ASSIGNMENT HELP AND HOMEWORK WRITING SERVICES AT CHEAPER RATE!
Question 5. The following image shows the values in grayscale. Perform the necessary steps to detect minutiae points. You don't need to detect any minutiae centered at the edge. Show your steps. Your result will include the coordinate of detected minutiae points and their types.
Answer:
%Program Description
%This program extracts the ridges and bifurcation from a fingerprint image
%Read Input Image
binary_image=im2bw(imread('input_1.tif'));
%Small region is taken to show output clear
binary_image = binary_image(120:400,20:250);
figure;imshow(binary_image);title('Input image');
%Thinning
thin_image=~bwmorph(binary_image,'thin',Inf);
figure;imshow(thin_image);title('Thinned Image');
%Minutiae extraction
s=size(thin_image);
N=3;%window size
n=(N-1)/2;
r=s(1)+2*n;
c=s(2)+2*n;
double temp(r,c);
temp=zeros(r,c);bifurcation=zeros(r,c);ridge=zeros(r,c);
temp((n+1):(end-n),(n+1):(end-n))=thin_image(:,:);
outImg=zeros(r,c,2);%For Display
outImg(:,:,1) = temp .* 204;
outImg(:,:,2) = temp .* 204;
outImg(:,:,3) = temp .* 204;
for x=(n+1+10):(s(1)+n-10)
for y=(n+1+10):(s(2)+n-10)
e=1;
for k=x-n:x+n
f=1;
for l=y-n:y+n
mat(e,f)=temp(k,l);
f=f+1;
end
e=e+1;
end;
if(mat(2,2)==0)
ridge(x,y)=sum(sum(~mat));
bifurcation(x,y)=sum(sum(~mat));
end
end;
end;
% RIDGE END FINDING
[ridge_x ridge_y]=find(ridge==2);
len=length(ridge_x);
%For Display
for i=1:len
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3):(ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)-3),2:3)=0;
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3):(ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)+3),2:3)=0;
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3),(ridge_y(i)-3):(ridge_y(i)+3),2:3)=0;
outImg((ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)-3):(ridge_y(i)+3),2:3)=0;
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3):(ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)-3),1)=204;
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3):(ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)+3),1)=204;
outImg((ridge_x(i)-3),(ridge_y(i)-3):(ridge_y(i)+3),1)=204;
outImg((ridge_x(i)+3),(ridge_y(i)-3):(ridge_y(i)+3),1)=204;
end
%BIFURCATION FINDING
[bifurcation_x bifurcation_y]=find(bifurcation==4);
len=length(bifurcation_x);
%For Display
for i=1:len
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3):(bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3),1:2)=0;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3):(bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)+3),1:2)=0;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3):(bifurcation_y(i)+3),1:2)=0;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3):(bifurcation_y(i)+3),1:2)=0;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3):(bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3),3)=204;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3):(bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)+3),3)=204;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)-3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3):(bifurcation_y(i)+3),3)=204;
outImg((bifurcation_x(i)+3),(bifurcation_y(i)-3):(bifurcation_y(i)+3),3)=204;
end
figure;imshow(outImg);title('Minutiae');
NEVER MISS YOUR CHANCE TO EXCEL IN CIS 663 BIOMETRICS ASSIGNMENT! AVAIL AFFORDABLE AND RELIABLE CIS 663 BIOMETRICS ASSIGNMENTS HELP SERVICES OF EXPERTSMINDS.COM
Avail the Syracuse University Assignment Help Services for related units and courses such as:-
- CIS 554 Object Oriented Programming in C++ Assignment Help
- CIS 531 Compiler Construction Assignment Help
- CIS 583 Systems Assurance Seminar Assignment Help
- CIS 545 Introduction to Combinatorics Assignment Help
- CIS 553 Software Systems Implementation Assignment Help
- CIS 581 Concurrent Programming Assignment Help
- CIS 565 Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks Assignment Help
- CIS 567 Knowledge Representation and Reasoning Assignment Help
- CIS 543 Control of Robots Assignment Help